Japan and South Korea
Home > Our Services > Certification > Product Certification > Electrical and Electronic Product Certification > Japan and South Korea

Products involving wireless devices shall be certified by GITEKI with the GITEKI mark and certificate number printed on the label attached to the product. Without such certification, selling these products directly in Japan is illegal and punishable by severe penalties.GITEKI certification is mandatory.
GITEKI certification is implemented on basis of the "Radio Act" (で ん ぱ ほ う) and the Act of Electrical Communication Industry (でんきつうしんじぎょうほう) promulgated by the Affairs Ministry (そ う む し ょ う), (full name of Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications in English, MIC for short), therefore, GITEKI is also called MIC certification.
JATE and TELEC are two of the RCBs approved by MIC. That is, both JATE and TELEC certifications are in fact GITEKI certification.
TELEC Certification
TELEC certification provides type approval of designated radio equipment in accordance with the requirements of the Radio Act (i.e., technical regulatory compliance certification). Such certification is mandatory and the certification body shall be the registered certification body recognized by MIC in the designated radio equipment scope.
TELEC (Telecom Engineering Center) is the main recognized certification body for compliance certification of radio equipment in Japan. It was the first legal authority in Japan to conduct radio law certification in the early stage, so many people mistakenly believed that the GITEKI certification was the TELEC certification. In fact, TELEC was only able to certify radio waves of GITEK in the early days, but not the telecommunications industry. However, TELEC finally got the certification qualification of Japanese Telecommunication Industry in July 2014.
JATE
"JATE" certification is a mandatory certification of access to the Japanese telecommunication network according to the requirements of the Act of Electrical Communication Industry. In brief, JATE certification is the network access certification in Japan.
JATE, the Japan Approvals Institute for Telecommunications Equipment, registered in April 1985 and was the first legal authority in Japan to conduct the certification of the Act of Electrical Communication Industry in the early stage, so many people mistakenly believed that the GITEKI certification was the JATE certification. In fact, so far, JATE has only certified telecommunications industry, not accepted the certification of radio waves.
Difference
|
|
TELEC | JATE |
|---|---|---|
| Different laws and regulations | Radio Law of Japan | Telecommunication Law of Japan |
| Different control scopes | Radio equipment | Telecommunications equipment |
| Different test contents | RF test | Signaling interaction test |
| Different characters in label | “R” character | “T” character |
Mark
TELEC and JATE certifications have different mark requirements, and the GITEKI Mark and certificate number must be embodied in the label attached to the certified products. TELEC and JATE marks consist of GITEK Mark + Symbol + Identification Code.

a.TELEC Mark
The TELEC symbol is "R" and Identification code format is AAA-jjxxxx
R: Represents Radio; AAA: Code of the RCB; jjxxxx: certificate number of the organization.
The TELEC mark and certificate number of the certifying authority which we cooperate with are shown as follows:
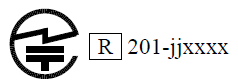
b. JATE Mark
The JATE symbol is "T" and Identification code format is x yynnnn AAA
T: Terminal equipment; x: category of specified terminal equipment;;
yynnnn: Certificate number of the organization; AAA: Code of the RCB;
The JATE mark and certificate number of the certifying authority which we cooperate with are shown as follows:

c. Size of giteki Mark:
The size of the mark shall be 3 mm or more in diameter. In case of equipment having a volume of 100 cc or less, the size shall be 3 mm or more in diameter.


Applicable district:Japan
Certification :VCCI
Certification overview:VCCI is Japan's electromagnetic compatibility certification mark, managed by Japan's Electromagnetic Interference Control Council (Voluntary Control Council for Interference by Information Technology Equipment), VCCI is voluntary certification, but information technology products sold in Japan, will generally be required to carry out VCCI certification.
Certification Procedure :

Note*:Ti Group is one of the VCCI members.
Certification Introduction
The Ministry of Knowledge Economy (MKE) announced on 25 August 2008 that the National Standards Committee (NSC) would implement a new national uniform certification markfrom July 2009 to December 2010. The new mark is called KC Mark, staning for Korea Certification. The current 13 compulsory certification marks will eventually be unified under the new mark. This measure can reduce the certification fees of suppliers and make KC mark gradually become a world brand certification.
KC Mark
KC mark (compulsory and self-discipline)
KC mark depends on the product size
The KC mark can be easily distinguished from the label of product or container and packaging, and is firmly printed or engraved and does not easily fall off.
The KC certification number is identified adjacent to the KC certification cover. Other matters relating to safety standards are noted in Chinese or English

Content on mark
Safety certification mark and safety certification number or voluntary safety confirmation mark and voluntary safety confirmation number
Product name (identified with legal Korean name)
Model
Electrical rated value(rated voltage, rated current, input power, output power, frequency, capacity, etc.)
Name of manufacturer (indicating country of manufacture for foreign enterprise)
Double-insulation product  for mark
for mark
Rated time (short time rating: when in compliance)
Date of manufacture (e.g.; date of manufacture (year/ month), batch number, etc.)
After-sales service (A/S) Korea Liaison Office (e.g.,telephone number, etc.)
EMI or EMI/EMS MARK(products passing the test ) (optional)
Other individual safety precautions: The operating manual in Korean must be provided.
Examples

Product List
KC Mark Certification Products List (list of KC products)
According to the Safety Management Law of Electrical Supplies in South Korea, safety certification of electrical supplies is divided into compulsory certification and self-regulatory (voluntary) certification since January 1, 2009.
Compulsory certification means that all electronic products belonging to the mandatory products must obtain KC before they can be sold in the Korean market and shall be subject to factory inspection and product sampling test every year. "Electrical appliances subject to safety certification" are electrical appliances that are prone to fire and electric shock and other hazards and obstacles due to factors such as structure or use method.
Self-regulatory (voluntary) certification means that all electronic products belonging to the voluntary products only need to be tested to obtain the certificate, and do not need to be subject to factory inspection. The certificate is valid for 5 years. "Electrical appliances subject to self-regulatory (voluntary) safety certification" refer to electrical appliances that have relatively simple product structure and use method, are not easy to cause fire shock and other greater danger and obstacles and can be tested to prevent the occurrence of hazards.




